Koa初探
特性
洋葱模型
koa是一个轻量级的nodejs后端模型,使用洋葱模型,对node的http模块进行了一个封装,可以方便地进行组合与编写中间件。
一个基本的洋葱模型实例如下:
typescript
const app = new Koa();
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
console.log(1);
await next();
console.log(3);
});
app.use(async (ctx, next) => {
console.log(2);
});
app.listen(3000);
// 输出依次为 1 2 3它的中间件执行会首先按顺序,遇到next则往下执行,执行完成后回到next的位置往下执行,像函数执行栈一样遇到next则推入执行,如同一个洋葱。
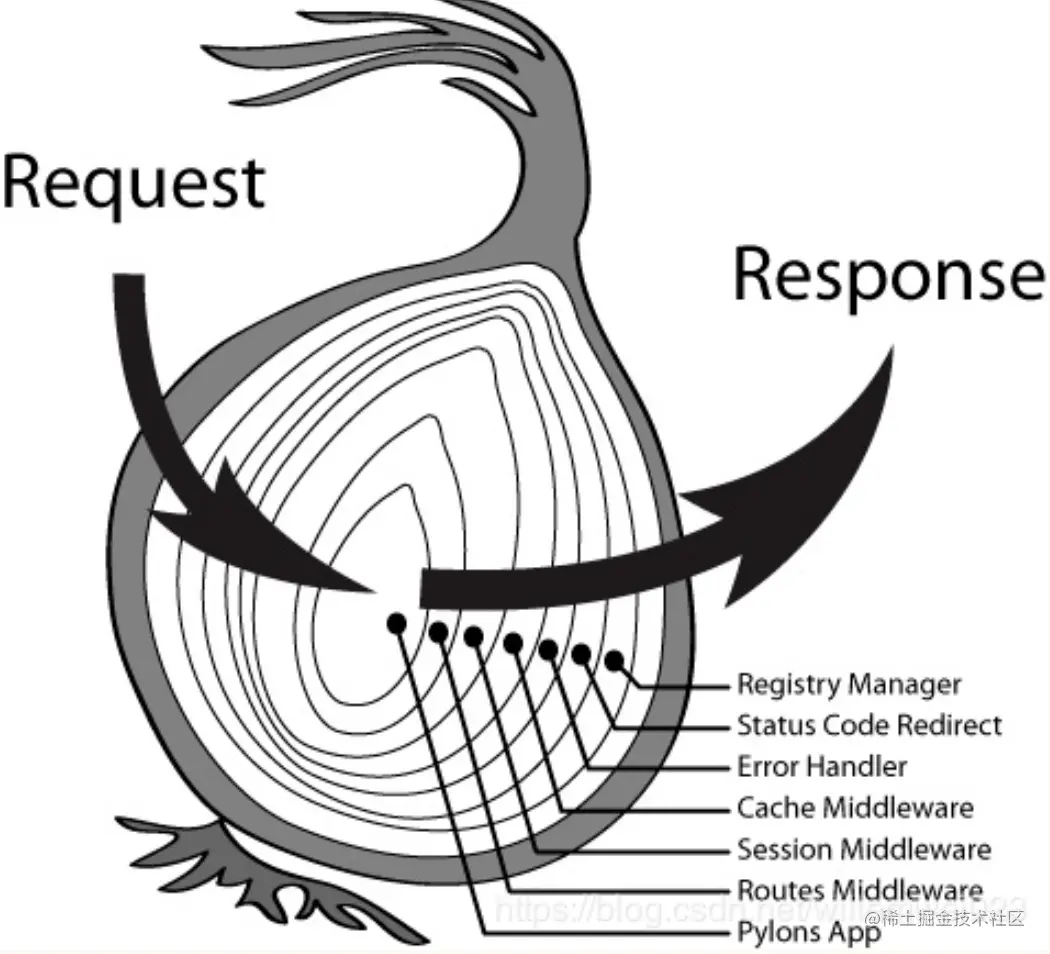
这是koa的精髓所在,可以方便地基于此特性组合中间件,如logger:
typescript
export default function logger() {
return async function (ctx: ParameterizedContext, next: Next) {
const start = +new Date();
await next();
const ms = +new Date() - start;
console.log(`耗时${ms}`ms);
};
}
app.use(logger());将此中间件作为第一个use,则可以方便计算出完整请求的执行消耗时间。
一些封装
koa对http模块的常用部分使用了get与set代理,便于以如下形式访问属性:
typescript
ctx.method
// ctx.request.method此外,还有一些直观的http上下文方法:
typescript
ctx.body = {
text: 'test'
}
// 使请求响应此json内容
ctx.url
// 请求urlKOA做的工作是处理了request和response对象,进行了代理操作,这样就可以方便地在同一个context对象上进行http的相关操作。
实践
可以简单地做一个对Application类的封装:
typescript
export class App {
private middlewares: MiddlewareFunc[];
context: Context | undefined = undefined;
private createContext(req: http.IncomingMessage, res: http.ServerResponse) {
const context = new Context(req, res, this);
this.context = context;
return context;
}
private callback() {
// 将所有中间件组合为一个函数用于执行
const fn = compose(this.middlewares);
return ((req, res) => {
const ctx = this.createContext(req, res);
// 处理request
handleRequest(ctx, fn);
}) as RequestListener;
}
constructor() {
this.middlewares = [];
return this;
}
use(middleware: MiddlewareFunc) {
if (typeof middleware !== 'function') {
throw new Error('Middleware must be a function');
}
this.middlewares.push(middleware);
return this;
}
listen(port: number) {
console.log(`Server is running on port ${port}`);
return http.createServer(this.callback()).listen(port);
}
}其中,整体的应用实例执行流程在于handlRequest函数,是获取context > 执行组合的中间件 > 处理response 的顺序流程,其实现为:
typescript
export function handleRequest(ctx: Context, fn: ComposedFunc) {
fn(ctx).then(() => {
handleResponse(ctx);
}).catch(() => {
...
});
}而对于由中间件组合而成的执行函数,通过Promise合为一个有顺序执行能力的异步函数:
typescript
export function compose(middlewares: MiddlewareFunc[]): ComposedFunc {
middlewares.forEach(((item, index) => {
if (typeof item !== 'function') {
throw new Error(`compose: middlewares must be an array of functions, got ${typeof item} at index ${index}`);
}
}));
return function(ctx) {
let index = -1;
return dispatch(0);
// 将所有中间件合为Promise的链式调用
function dispatch(i: number): Promise<void> {
if (i < index) {
throw new Error(`compose: next() called multiple times`);
}
index = i;
let func: MiddlewareFunc | null = middlewares[i];
if (i >= middlewares.length) {
func = null;
}
if (!func) {
return Promise.resolve();
}
return Promise.resolve(
// 此处bind的dispatch即为中间件接收到的next函数,其功能为调用下一个中间件并依次执行返回后返回next调用位置
func(ctx, dispatch.bind(null, i + 1))
);
}
}
}